Equilibrium Rate Of Return Formula
16.3 Forex Equilibrium with the Rate of Return Diagram
Learning Objective
- Apply the rate of return plots to represent the interest rate parity equilibrium in the strange exchange market.
An culling graphical approach is sometimes used to depict the equilibrium substitution rate in the strange commutation (Forex) market. The graph is called the rate of return diagram since information technology depicts rates of return for avails in two separate countries every bit functions of the exchange rate. The equilibrium condition depicted in the diagram represents the involvement rate parity condition. In issue, the diagram identifies the equilibrium commutation rate that must prevail to satisfy the involvement charge per unit parity condition.
Think the charge per unit of return formulas for deposits in two separate countries. Consider an investor, holding U.S. dollars, comparing the purchase of a one-year certificate of deposit (CD) at a U.S. bank with a one-year CD issued by a British bank. The rate of return on the U.S. deposit works out simply to be the U.S. interest charge per unit shown below:
RoR $ = i $.
The rate of render on the British asset, however, is a more complicated formula that depends on the British involvement rate (i £), the spot commutation rate (Eastward $/£), and the expected exchange rate (E $/£ e ). In its simplest form it is written equally follows:
In Figure 16.5 "Rate of Return Diagram", we plot both RoR equations with respect to the exchange rate (E $/£). Since RoR $ is not a function (i.e., not dependent) on the exchange charge per unit, information technology is drawn as a vertical line at the level of the U.S. interest rate (i $). This but means that every bit the commutation rate rises or falls, the RoR $ ever remains immutably fixed at the U.S. interest rate.
Figure 16.5 Rate of Return Diagram
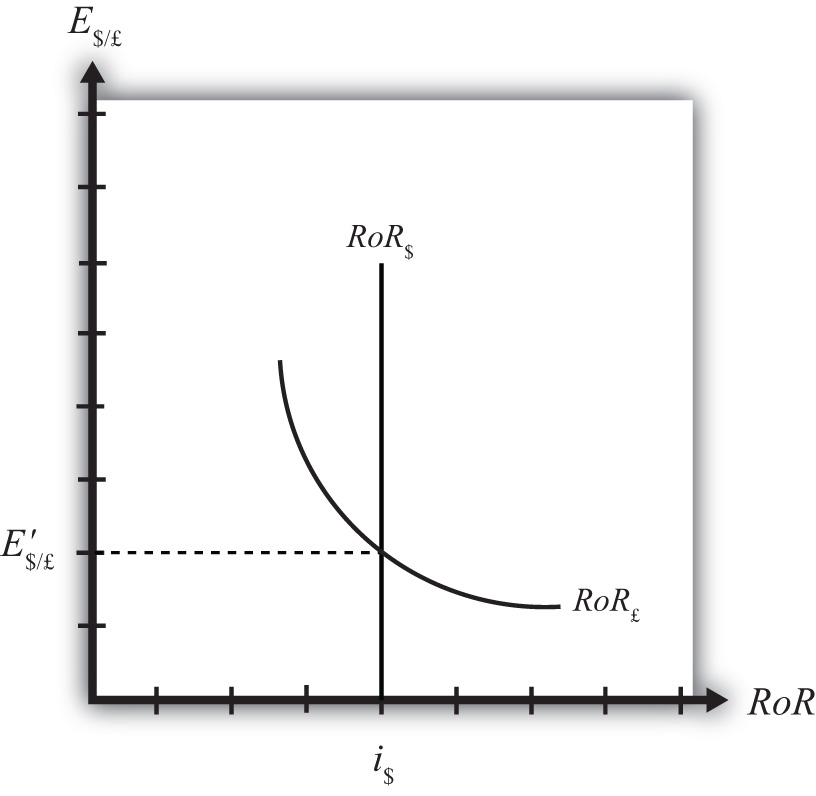
The RoR £, however, is a function of the commutation rate. Indeed, the relationship is negative since E $/£ is in the denominator of the equation. This means that every bit E $/£ rises, RoR £ falls, and vice versa.
The intuition backside this negative relationship is obtained past looking at the culling (equivalent) formula for RoR £:
Recall that the exchange rate ratio represents the expected percentage change in the value of the pound. Suppose, every bit an example, that this term were positive. That would mean the investor believes the pound will appreciate during the term of the investment. Furthermore, since it is an expected appreciation of the pound, information technology volition add to the total rate of return on the British investment. Adjacent, suppose the spot substitution rate (East $/£) rises today. Assuming ceteris paribus, as nosotros always do in these exercises, the expected exchange charge per unit remains fixed. That will mean the numerator of the exchange rate expression volition fall in value, as will the value of the unabridged expression. The estimation of this modify is that the investor'due south expected appreciation of the pound falls, which in turn lowers the overall rate of render. Hence, we become the negative human relationship between the $/£ exchange rate and RoR £.
The intersection of the ii RoR curves in the diagram identifies the unique exchange rate E′$/£ that equalizes rates of return betwixt the two countries. This substitution rate is in equilibrium because any deviations abroad from interest rate parity (IRP) volition motivate changes in investor behavior and strength the exchange back to the level necessary to achieve IRP. The equilibrium adjustment story is next.
Primal Takeaways
- The rates of return are plotted with respect to the exchange rate. The domestic rate of render does not depend on the exchange rate and hence is drawn as a vertical line. The foreign rate of render is negatively related to the value of the strange currency.
- The intersection of the rates of return identifies the substitution charge per unit that satisfies the involvement rate parity condition.
Exercise
-
Jeopardy Questions. Every bit in the popular boob tube game show, you are given an answer to a question and you lot must respond with the question. For instance, if the answer is "a tax on imports," and so the correct question is "What is a tariff?"
- Of positive, negative, or zero, the relationship betwixt the U.Due south. interest charge per unit and the charge per unit of return on U.South. avails.
- Of positive, negative, or zero, the human relationship between the exchange rate (E $/£) and the rate of return on U.Due south. assets.
- Of positive, negative, or naught, the human relationship between the commutation rate (E $/£) and the rate of render on British assets.
- The name of the endogenous variable whose value is determined at the intersection of two rate of return curves.
Equilibrium Rate Of Return Formula,
Source: https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_international-economics-theory-and-policy/s19-03-forex-equilibrium-with-the-rat.html
Posted by: davidsonnoby1984.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Equilibrium Rate Of Return Formula"
Post a Comment